Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 (MEN2) is an autosomal dominant disease that occurs because of germline pathogenic variants in the rearranged during transfection (RET) proto-oncogene. The RET gene was isolated in 1993 and pathogenic variants affect 1–10 per 100,000 people. Approximately 50% of cases are de novo.
Cancer Risk by Phenotype
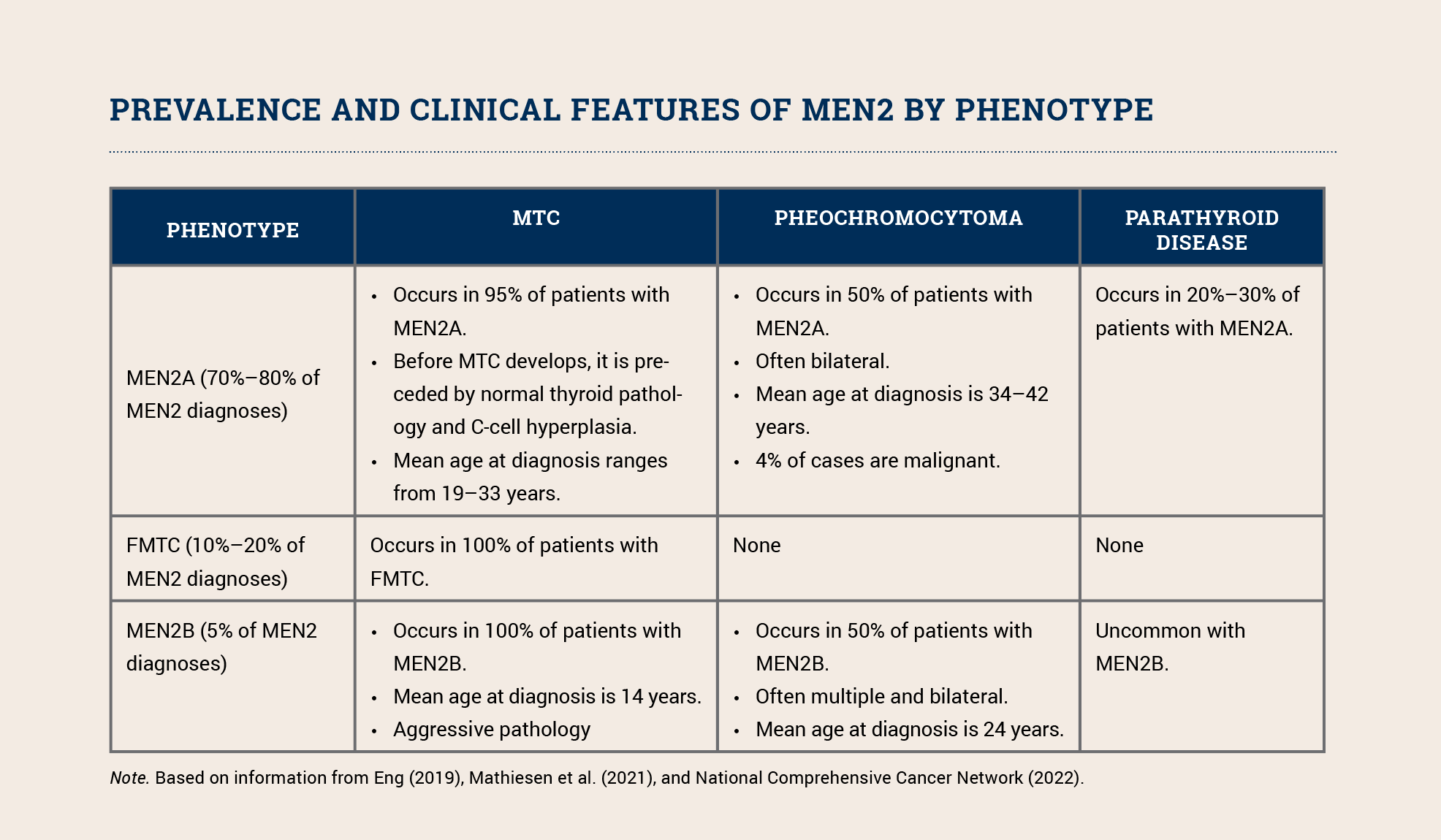
MEN2 includes three phenotypes: MEN2A, the familial medullary thyroid carcinoma (FMTC) variant of MEN2A, and MEN2B. All three phenotypes increase a patient’s risk for developing medullary carcinoma of the thyroid (MTC); MEN2A and MEN2B also increase the risk for pheochromocytoma and parathyroid tumors (see sidebar). MEN2B’s other clinical features include distinctive facial features (i.e., lips becoming more prominent as a child grows), mucosal neuromas, and ganglioneuromatosis of the gastrointestinal tract. The phenotype depends on the specific pathogenic variant.
Although MTC accounts for only 5% of all thyroid cancer cases, it is responsible for 15% of all thyroid cancer deaths. MTC is aggressive and associated with an increased risk of metastasis to the lungs, liver, and bones. About 25%–30% of all individuals with MTC have a germline RET pathogenic variant. Because of their increased risk for morbidity and mortality, all patients with MTC should be offered testing for pathogenic RET variants. Those who test positive should be educated about risk-reducing thyroidectomy and other intensive screening as well as cascade testing for other family members so they can clarify their individual risk and engage in prevention and early detection measures.
Prevention
Because of the significant morbidity and mortality associated with MTC, pheochromocytoma, and parathyroid disease, prevention is the best management strategy for MEN2.
Prophylactic thyroidectomy is recommended for individuals with an identified germline RET pathogenic variant. Depending on the specific pathogenic variant, this can be recommended for patients as young as 6 months to 1 year. Infants from families with a known pathogenic variant should be tested at birth.
Prior to surgery, patients with MEN2A or MEN2B should obtain biochemical screening, including measurement of catecholamine and metanephrine levels, to exclude a functioning pheochromocytoma. Similarly, females with MEN2 should be screened for pheochromocytoma prior to planned pregnancies or as early as possible during unplanned pregnancies to reduce complications from a hypertensive crisis. Dopamine D2 receptor antagonists and beta-adrenergic receptor antagonists are contraindicated in patients with MEN2 and pheochromocytoma because of a high risk for adverse reactions.
Early Detection
Patients with MEN2 should also have regular surveillance, including:
- Annual calcitonin concentration levels to detect residual or recurrent MTC after thyroidectomy, even if thyroidectomy was performed prior to biomarker evidence of disease
- Monitoring for possible hypoparathyroidism (for thyroidectomy and parathyroid autotransplantation)
- Annually beginning at age 8:
- Biochemical screening in individuals who were initially negative for pheochromocytoma, including 24-hour urine collection for catecholamines and metanephrines, neck ultrasound, and chest and abdominal computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging as required
- Biochemical screening for parathyroid adenoma, including serum calcium, parathyroid hormone, 25-hydroxyvitamin D3, calcitonin, and metanephrines
Nursing Implications
Management of MEN2 requires ongoing lifetime screening beginning in infancy. Families need psychosocial support and a consistent team of providers to implement prevention and detection measures.
Individuals should be educated about the following symptoms to report and evaluate promptly:
- High or variable blood pressure, especially spiking blood pressure
- Increase in headache frequency or intensity
- Increased sweating or what feels like a panic attack, fear, or anxiety
- Irregular or rapid heartbeat
Recognizing MEN2 syndromes and referring all individuals with MTC for genetic assessment allow patients and providers to initiate screening and preventive surgery, which significantly reduces associated morbidity and mortality.